Finding complications and improving the structure of the organization
Experience has shown that the success or failure of organizations directly depends on the quality and effectiveness of their employees. Today’s successful organizations have come to the conclusion that in order to compete in global markets, they must have global human resource management. A complete understanding of the current state of the organization and finding organizational complications helps greatly in reducing their costs, and identifying organizational complications and the causes of these complications is the first step in analyzing the organization. The purpose of troubleshooting is to identify the problems in the organization and provide appropriate and practical solutions to solve them.
The Asian Productivity Organization, based on its studies and researches, has identified the complications and factors preventing the improvement of productivity at the level of Asia, and Productivity Management, based on its studies, researches and experience and according to the existing conditions in Asia, has identified some factors has added that in total it is as follows:
- Human problems
- Poor work culture
- The low level of knowledge of most employees
- Insufficient and ineffective communication between different work categories
- Lack of sense of responsibility and compassion and lack of work motivation for both managers and employees
- The lack of proper use of human resources and the absence of a proper training program in accordance with the company’s goals
- Not having the necessary work skills
- Resistance to change from management and employees
- lack of commitment and participation (lack of spirit of participation of personnel in work issues and problems)
- Financial problems
- Liquidity and financing problems
- Lack of marketing for products and lack of knowledge of the market and evaluation of competitors
- Non-allocation of budget and optimal funds, in the case of multi-product units
- Technical problems
- Non-standard production
- Low quality products and services
- Old and outdated technology, machinery and production process
- Low production rate compared to the nominal capacity due to various reasons
- Very low capital utilization
- The problem of obtaining raw materials at the right time for production
- The high level of waste and production stoppage for various reasons
- Not being active and not valuing design and research departments and not paying attention to technical knowledge (technology)
- Management problems
- Instability of managers
- Lack of efficiency of management information systems
- Level and cross-sectional decisions by managers
- Lack of information about technology, standards and productivity indicators
- Failure to attract efficient human resources
- Lack of interest in the development and welfare of human resources
- Spending a large amount of time on trivial matters
- Ownership decisions by managers for the entity under supervision
- Organizational, organizational and planning problems
- Lack of correct and controlled organizational chart
- Absence of a strict control system to evaluate the performance of managers
- Appointing managers according to non-specialized aspects and not paying attention to their efficiency
- Absence of a quality system for directing, controlling and monitoring funds
- Giving too much importance to the headquarters personnel than the production personnel
- The lack of a clear plan and the adoption of some problematic policies for the unit
- Ownership decisions by managers for the entity under supervision
- State law problems
- Inconsistency of the rules with the problems of the units
- Inconsistency of the established rules with the economic operations required by the units
- The complexity of laws and guidelines and their ineffectiveness
Now, according to the mentioned cases, the continuation of this situation will be associated with the decline of the country’s position in the world economy, as well as a decrease in the quality of life and an increase in unemployment. Therefore, the analysis of the effective factors in the formation of these challenges and how to solve them will not be possible without the effective participation of all those involved. For this, it is necessary to get an understanding of the expectations and performance of the organization and determine the gap between the two, the existence of this gap indicates the existence of complications in the organization, which need to be identified. In order to understand and recognize the existence of a gap between the expectations and the performance of the organization, it is necessary to find complications in the organization.
In the process of finding complications and according to the logic of gap analysis, three basic phases must always be implemented sequentially:
The phase of recognition, evaluation, analysis and explanation of the existing situation in the organization
The design phase and the explanation of the desired (expected) situation in a certain period of time
The phase of planning and action to move from the current situation to the desired situation
The first step: collecting general information about the organization
The second step: examining the nine domains of performance results included
- Effectiveness
- Efficiency
- productivity
- Innovation
- Flexibility
- Customer satisfaction quality
- Quality of work life
- profitability
- social responsibility
The third stage: examination of the internal areas and territory of the organization included
- Mission field, vision, long-term goals, strategies and policies
- The field of processes
- The field of organizational structure and organization
- The field of systems and methods
- Area of operational space
- The field of production technology
- Examining the territory (external environment) of the organization includes:
- Customers
- Competitors
- Suppliers
- Distributors
- market situation
Fourth step: Identifying complications, causes and roots of problems and prioritizing them
The fifth step: Summarizing the evidence of the existence of complications and extracting the main complications in the field of performance results
The sixth stage: Establishing cause and effect relationships between complications and the main causes of their occurrence and providing primary solutions based on complication detection, to eliminate or reduce complications.
Areas of results
Areas that make up the results reflect the performance of the entire organization. The output and fruit of the organization in the use of resources and enablers can be seen in the form of characteristics and signs in the field of results.
- Effectiveness: The areas that make up the results show the performance of the entire organization. The output and fruit of the organization in the use of resources and enablers can be seen in the form of characteristics and signs in the field of results.
- Efficiency: Doing things right is called efficiency. Another definition of efficiency is how much resources can be used in the desired way and is calculated from the following formula.
- Productivity: It is one of the most important indicators in the organization that states how much of the consumed resources have produced the outputs and products. In other words, productivity is the sum of efficiency and effectiveness. Productivity is mainly divided into two types: general productivity and partial productivity (specific to each case). Productivity is calculated in several ways, the most important of which are:Profitability: The main goal and purpose of every organization is profitability, which mainly indicates the achievement and movement of the organization in the direction of facilitating and achieving the predicted profit. There are many indicators to determine it, among them, the percentage of profit realization can be mentioned.
- Quality and customer satisfaction: The term quality means considering quality characteristics and applying them to materials (including consumable raw materials, semi-finished products, and finished products), production processes, etc., in order to ensure that the characteristics, expectations, and demands of the product are met. The customer’s opinion is even in the categories of timely delivery, after-sales service and reasonable price. To achieve this, it is necessary to use techniques and methods in this direction.
Extracting tokens from result domains
At this stage, the aim is to examine the nine areas of results in order to understand the signs of the organization. Signs have the following characteristics:
- They are visible, obvious and tangible
- They are in the surface layers and not in depth
- can be understood by ordinary people
These signs are a guiding light to show the starting and target points in the future horizon of a movement in the complication tree and are the origin of the next movements to identify the complications and then the causes related to it. The way to extract the signs is that the questions of the checklists designed in the areas of the results are completed by discussing with the expert committees and from them and generally relying on figures and statistics (if any), the signs are extracted.
Checking the environment and leveling
Today, no organization can continue its competitive life without considering the effects and changes of environmental conditions. Increasing global competition and reducing the distance between producers have caused organizations to study and identify the environment and competitors every moment and monitor the environment to identify opportunities and threats.
Determining the complications of the organization
As mentioned, the signs of the organization are a series of raw evidences that indicate the presence or absence of a problem in the organization. In general, extracting and determining side effects from symptoms requires special expertise and experience and is obtained from examining the following areas:
- Examining the environment and external influencing factors
- Examination of the organization in the field of enablers
Investigating the causes of complications and determining the root causes and improvement opportunities
Definitely, the solution to solving the problem and defect is to find its origin and cause. After extracting the complications, it is necessary to analyze the causes that cause it in different layers in the field of enablers and display their connections in a logical form. This is done until the causes are obtained. Rooting continues, the main tools used are cause and effect diagrams and communication networks. At this stage, by examining the enablers, other complications or opportunities for improvement in different areas can be obtained.
Determining solutions to eliminate root causes and eliminate complications
This stage is the presentation of treatment, method and mechanism to be prescribed in the framework of the related causes and complications as a corrective solution to eliminate the root cause. The solution can be physical and hardware or informational and software. In addition, it can be very simple and limited, or it can be a set of operations and activities in the form of a vast project that includes different levels of the organization.
The schematic of connections between symptoms in the field of results, complications and root causes in the field of resources and enablers, and corrective solutions and opportunities for improvement are presented in the figure below.
Prioritizing complications and solutions
Complications are prioritized with the aim that the organization’s power is more concentrated in the most important and important areas and the dispersion of resources on all activities, projects and corrective measures at a specific time is avoided and the organization’s resources are used in order to solve acute and major problems. be spent
Planning the implementation of the proposed solutions
At this stage, a suitable schedule is applied in order to better manage and control solutions. The purpose of planning the implementation of the proposed solutions is to determine the implementation time, required resources and planning for the implementation of projects (solutions) and predicting the results.
summary
At this stage, the results of the recognition and analysis of the existing situation of the organization under the title of existing problems and problems and the proposed solutions to solve and reduce them are organized and presented in a comprehensive and accurate manner, so that the problem-finding cycle can be implemented again and the path of excellence walk
Models of problem solving and organizational excellence:
In order to measure the superiority of organizations and find out the current and relative position in which they are placed, it is necessary to identify the issues and problems affecting the organization so that their position can be compared to each other. For this purpose, there is a need for models and tools that help and accelerate this movement. Below are some examples of them.
European Foundation for Quality Management (EFQM) model
The EFQM model is an executive tool to help organizations to ensure the establishment of a suitable management system by measuring the level of being on the path of sustainability and has helped organizations to identify gaps and then determine solutions with better motivation. In this model, the organization is examined in the fields of enablers and results and is evaluated based on a reasoned logic.
Balanced score card (BSC) model
The BSC model is a conceptual framework whose task is to translate the company’s strategic goals into a set of performance indicators. These indicators are usually selected from among the four aspects of finance, customer, internal processes, and learning and growth, and then they are scored in the framework of a specific path.
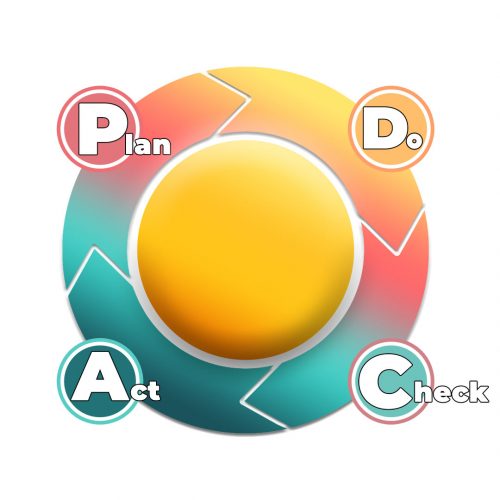
Deming cycle model (PDCA)
The use of the Deming cycle model is applicable to all parts of the organization and helps the managers of the organization to find complications at the moment they arise.
Weissboard model
This model shows managers which parts to look for in the organization to diagnose complications. Of course, the Weisboard model specifies the general parts, and the organization managers are responsible for determining the details. The components of this case of organizational complication models are:
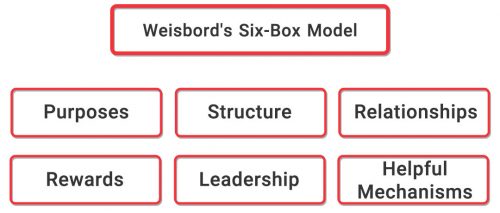
- Organizational communication includes interpersonal communication and communication between different parts of the organization
- Organizational goals
- Organization structure
- Reward system
- Application processes
- leadership
Six Sigma model
The Six Sigma model has three main factors, which are:

- Strategies and organizational strategies
- Strategies implementation techniques and measures
- Organizational culture
In this method, organizational troubleshooting goes through the process of definition, measurement, analysis, promotion and control. The reputation of the six sigma model is due to the precise performance and optimal changes with the lowest cost. This model helps organizations to maintain the current values of the organization and achieve future success.
McKinsey model
James McKinsey is the CEO of McKinsey Management Consulting, which uses the corporate diagnostic model as a framework. This organizational problem solving model is one of the most famous models presented by McKinsey in the field of management, in which 7 of the most important factors for business problem solving are introduced. These seven items are:
- Strategy
- Shared values
- System
- Structure
- Organizational skills
- Management style
- Human resources
These models are complementary to each other, and by examining all of them, managers can be sure that they have identified all the layers of the organization.












